點狀資訊KML檔之撰寫(csv2kml.py)
Table of contents
背景
- 點狀資訊在KML架構中是最單純的。KML提供了點狀性質(feature)的設定方式,因此使得單調的點,因著背景地圖的參考而變得豐富。
- [csv2kml.py]的應用有很多,繪製軌跡圖、將點狀(與鏈結)資訊輸出到uMAP展現、貼在openTopo底圖(NCLonOTM)、ISC/AERMOD地理資訊的解讀展示等等。
- 如果要建立更複雜的KML,由熟悉點狀資訊的輸出,會是一個好的開始。
前言
csv是常見的資料表格式,KML則是google提供的語言介面,好讓使用者也可以在google map上貼圖,現已成為開放式地理空間協會地理資訊的編碼標準。 因此csv2kml顧名思義就是嘗試把一個存有座標的csv檔案,寫成kml檔案,最終能貼在google map、openstreet map等網路地圖上,完成這項工作的python小程式。(成果如附圖)
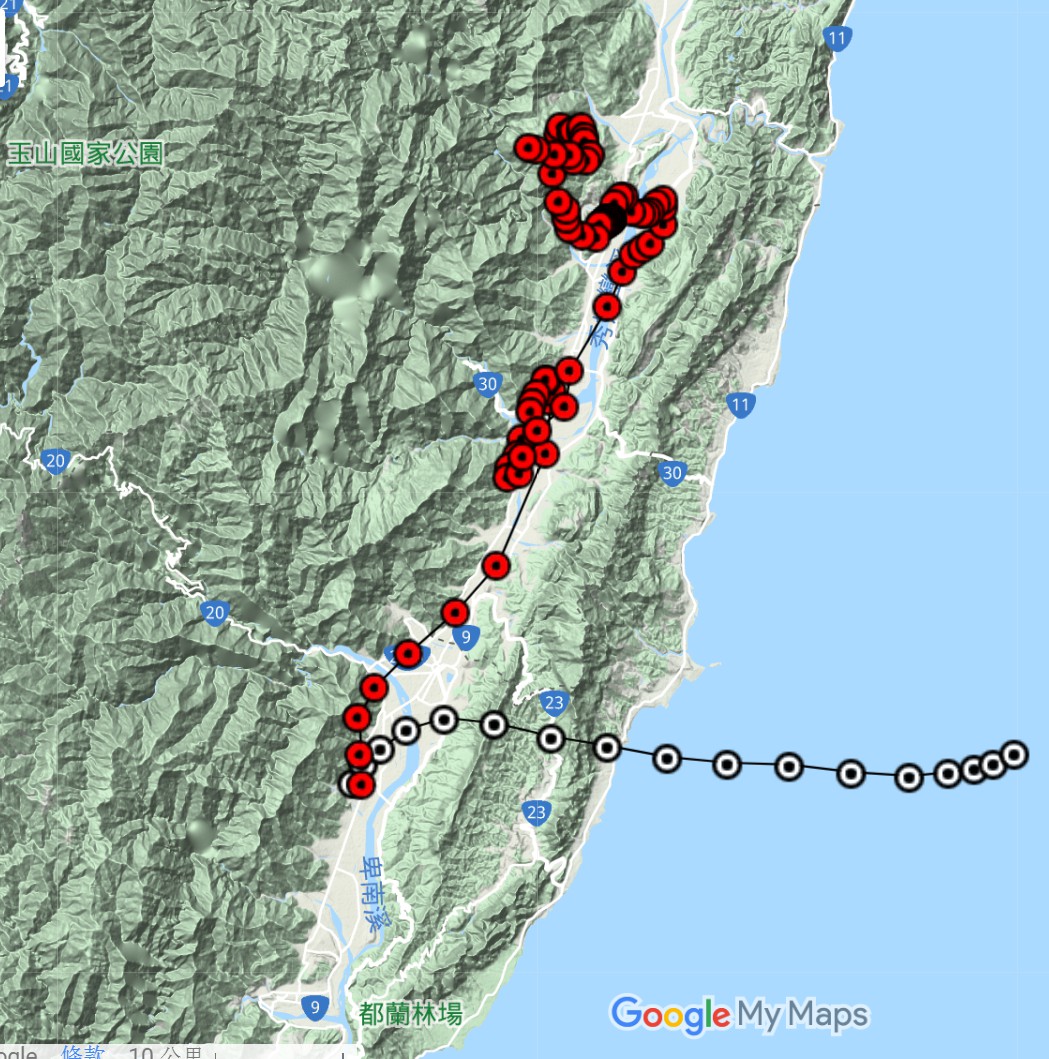 |
|---|
| csv2kml結果範例 |
- 輸入部分重點在於應用pandas模組來開啟csv檔案,呼叫csv的內容。其次則為處理命令列選項的模組argparse,這2者都是python資料處理常用的模組。
- 輸出部分是本程式的重點。主要參考KML官網的介紹,將要繪製的內容、點、線等元素,依據KML的順序寫出,以符合google map程式的規則。KML(Keyhole Markup Language)及其zip後的檔案格式KMZ,是google map/google earth平台上特有的檔案格式,詳細介紹可以參考官網及網友的說明。大致上KML語法和html相同,除了一般性的格式之外,在地圖上標示的元件以
… 做為起迄標示。而在本作業中乃是以LineString、Point 為繪圖形式,此外KML也有Path、Polygon(shaded色塊) 等形態。 - 處理計算部分google map用的是經緯度系統,台灣地區常用的是TWD97系統,如果使用後者,需要進行座標轉換。此處使用twd97模組。
KML格式及內涵
- KML的內容可以參考其教學網站。如果只需要輸出單一分開的功能,可以考慮simplekml模組。 範例圖檔(紅色部分)為如下共276行之kml檔案,kml並不需要跳行,純粹是為了閱讀解釋方便才加上跳行指令(‘\n’),其內容說明如下:
起始
在此說明整個檔案會用到的宣告,包括
- 開啟kml 及Document之宣告
- 名稱name(會出現在google map的圖名標籤)(line 1)
- 敘述說明descri(line 1)
- 可能會用到的圖像定義Icon(line2~6),是用style id 來定義並呼叫,範例呼叫了紅點reddotPlacemark。
- icon選擇的考量:
$ cat -n trjguanshan2019062315.csv.kml
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><kml xmlns="http://www.opengis.net/kml/2.2"><Document><name>trjguanshan2019062315.csv</name><descri ption>trjguanshan2019062315.csv</description>
2 <Style id="normalPlacemark"><IconStyle><Icon><href>http://maps.google.com/mapfiles/kml/paddle/</href>wht-blank.png</Icon> </IconStyle></Style>
3 <Style id="highlightPlacemark"><IconStyle><Icon><href>http://maps.google.com/mapfiles/kml/paddle/red-stars.png</href> </Icon> </IconStyle></Style>
4 <Style id="dotPlacemark"><IconStyle><Icon><href>http://maps.google.com/mapfiles/kml/pal4/icon57.png</href> </Icon> </IconStyle></Style>
5 <Style id="blackdotPlacemark"><IconStyle><Icon><href>http://maps.google.com/mapfiles/kml/pal4/icon25.png</href> </Icon> </IconStyle></Style>
6 <Style id="reddotPlacemark"><IconStyle><Icon><href>http://maps.google.com/mapfiles/kml/pal4/icon49.png</href> </Icon> </IconStyle></Style>
7 <Placemark><name>hour=0</name><description>ymd=2019062315</description><styleUrl>#reddotPlacemark</styleUrl><Point><coordinates>
8 121.16166338764377,23.04499756226396,0</coordinates></Point></Placemark>
9 <Placemark><name>hour=1</name><description>ymd=2019062314</description><styleUrl>#reddotPlacemark</styleUrl><Point><coordinates>
10 121.16052210969468,23.06644148767801,0</coordinates></Point></Placemark>
11 <Placemark><name>hour=2</name><description>ymd=2019062313</description><styleUrl>#reddotPlacemark</styleUrl><Point><coordinates>
12 121.15857390654217,23.090818981273667,0</coordinates></Point></Placemark>
13 <Placemark><name>hour=3</name><description>ymd=2019062312</description><styleUrl>#reddotPlacemark</styleUrl><Point><coordinates>
14 121.17029256991134,23.110768605923834,0</coordinates></Point></Placemark>
...
181 <Placemark><name>hour=87</name><description>ymd=2019062000</description><styleUrl>#reddotPlacemark</styleUrl><Point><coordinates>
182 121.28943947883455,23.47345566850706,0</coordinates></Point></Placemark>
183 <Placemark><name>hour=88</name><description>ymd=2019061923</description><styleUrl>#reddotPlacemark</styleUrl><Point><coordinates>
184 121.28348218711278,23.475183559469606,0</coordinates></Point></Placemark>
185 <Placemark> <LineString> <coordinates>
186 121.16166338764377,23.04499756226396,0
187 121.16052210969468,23.06644148767801,0
188 121.15857390654217,23.090818981273667,0
189 121.17029256991134,23.110768605923834,0
190 121.19588315665499,23.134448977175694,0
191 121.23013239723322,23.161453958196724,0
...
274 121.28348218711278,23.475183559469606,0
275 </coordinates></LineString></Placemark>
276 </Document></kml>
直線段落
第3段(line185~275)為範例圖檔中的「線」(LineString)。「線」指令會將給定座標的第1點開始,按照順序連接所有的座標點,直到最後1點。
33 df=read_csv(fname)#,encoding='big5')
47 col=df.columns
50 for i in range(len(df)):
51 nam=df.loc[i,col[2]]
52 desc=df.loc[i,col[3]]
55 if TWD97:
56 x,y=df.loc[i,col[0]],df.loc[i,col[1]]
57 lat,lon=twd97.towgs84(x,y)
58 if LL:
59 lon,lat=df.loc[i,col[0]],df.loc[i,col[1]]
座標轉換計算
- twd97
- 網友公開的twd97模組,其計算結果與學術單位網站服務所差小於1M
- 在119~121範圍內有效,其外結果則不保證。
多邊形的應用
基本
- 同樣2點以上的數據,可以用點(Point)或線(Line)形式來繪製KML的地標(Placemark)
- 4點以上,如果最後點與第一點重疊,則可以選擇以多邊形來展現地標,多邊形的特性就是除了線條之外,也可以針對填滿的顏色、透明度等進行設定。
- 等值圖KML檔之撰寫就是以具有順序的多邊形、來層疊出等值圖的特性。
多邊形的特殊約定
- 由於多邊形物件不限定點數,因此必須(至少)約定物件的開始點。
- 此處在df.desc內容中約定含有’p0’字串者,為該物件的第一筆,如此就可以正確切割csv檔案成為所要的多邊形群組,同時保有原來csv檔的單純性。
...
else: #Polygon case
headP = '</styleUrl><Polygon><outerBoundaryIs><LinearRing><tessellate>1</tessellate><coordinates>'
tailP = '</coordinates></LinearRing></outerBoundaryIs></Polygon></Placemark>'
ps=[i[-2:] for i in list(df[col[3]])]
npoly,i0,i1=1,[0],[len(df)]
if 'p0' in ps:
npoly=ps.count('p0')
if npoly>1:
i1=[]
for i in range(npoly-1):
i0.append(i0[-1]+1+ps[i0[-1]+1:].index('p0'))
i1.append(i0[-1])
i1.append(len(df))
for ip in range(npoly):
# level=int(np.random.rand()*10)
level=5
nam=df.loc[i0[ip],col[2]].replace('p0','')
desc=df.loc[i0[ip],col[3]].replace('p0','')
line.append('<Placemark><name>' + nam + '</name><description>'+desc+'</description><styleUrl>#level' + str(level) + headP)
print (i0[ip],i1[ip])
for i in range(i0[ip],i1[ip]):
line.append(lonlat[i])
line.append(tailP)
...
程式說明
csv2kml.py 程式碼
調用模組與引數之讀取
在命令列鍵入引數, python常用的讀取方式有2種,一者為簡易的sys.argv指令,另外最常使用的則是其內設的引數解析argparse模組。前者沒有help、不會解析引數的型態,一律為字串。相對而言,後者的功能就較為完整、足供應用了。使用argparser讓引數的種類可以多元化
本程式所需的引數有3個,分別為:
- -f(csv檔案名稱)、
- -n(點線型態的選擇、有N白色地點、H紅色地點、D細線圓點、R紅色圓點、B黑色暈點,再加L繪線、G則告訴程式csv的內容為多邊形 )
- -g座標系統有TWD97及LL 等2個選項
- LL為經緯度
- TWD97為台灣地區2度分帶97年基準座標
程式語法以add_argument()來接收命令列訊息。
- 必要的選項有2,選項代碼(短名)、選項長名、
- 其他補充的選項包括是否必須(required)、引數的類型、以及說明內容。
- 在呼叫時以3個元素的tuple來承接(line 16),其順序即為檔名、點線特性、以及座標系統種類。
$ cat -n ~/bin/csv2kml.py
1 #!/cluster/miniconda/envs/py37/bin/python
2 from pandas import *
3 import twd97,sys
4
5
6 def getarg():
7 """ read the setting of plot from argument(std input)"""
8 import argparse
9 ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
10 ap.add_argument("-f", "--fname", required = True, type=str,help = "csv xy data")
11 ap.add_argument("-n", "--NorH", required = True, type=str,help = "Normal/Highlight/Dot/Reddot/Blackdot w/o Line")
12 ap.add_argument("-g", "--GEOG", required = True, type=str,help = "LL or TWD9")
13 args = vars(ap.parse_args())
14 return args['fname'],args['NorH'],args['GEOG']
15
定義座標種類
- 標示方式可以是
- H:Hightlight Baloon
- N:Normal Baloon
- D: Dots
- R: Red Dots
- B: Black Corona
16 fname,NorH,geog=getarg()
17 NorH,geog=NorH.upper(),geog.upper()
18 LL,TWD97=False,False
19 if geog=='LL':
20 LL=True
21 if geog=='TWD97':
22 TWD97=True
23 if NorH[0] not in ['H', 'N', 'D','R','B'] :sys.exit('NorH not right')
24 NH=NorH.replace('L','')
25
26 #B:target with black arona
27 #R:red target
28 #D:dot target
29 stl={'N':'normalPlacemark','H':"highlightPlacemark",'D':"dotPlacemark",'B':"blackdotPlacemark",'R':"reddotPlacemark"}
30 #csv with 4 columns,
31 #xp,yp,Hour,ymdh
32 #266567.0,2549275.0,hour=0,ymd=2019062315
pandas之應用
- python讀取ASCII資料一般也有2種方式,一者開啟檔案後直接讀取(with open(fname,’r’) as file:;data=[l for l in file]),讀出來的內容一律是字串(含跳行指令’\n’),還必須另外分段、解析、給予型態定義。
- 另一方式則以pandas來讀取。在解析上方便太多。以一般具有表頭(header)、逗點分隔(delimitor)的csv檔而言,讀取指令最簡單如line 33所示。如果不是,也可以在一行內解決設定。
- python 3必須指定coding,python 2 則不需要
- pandas的資料結構(dataframe)具有陣列處理的功能,具有平行計算的能力,然本範例中仍然當成序列循續處理,也有淺顯易懂的好處。
- df.columns:讀取表頭成為一序列
- df.loc[i,j]:讀取資料表中i列(i為數字), j欄的內容(前述表頭欄位名稱之一)。
33 df=read_csv(fname)#,encoding='big5')
34 TITLE=fname
KML檔頭與標點
- 檔頭除了標示kml版本之外,也宣告了標點、線條的樣式
35 head0='<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><kml xmlns="http://www.opengis.net/kml/2.2"><Document>'+ \
36 '<name>'+TITLE+'</name><description>'+TITLE+'</description>'
37 #store the lines
38 line=[head0]
39
40 #icons may be used in KML file:
41 sty_pngs={'H':'paddle/red-stars.png','N':'paddle/white-stars.png','B':'pal4/icon25.png','D':'pal4/icon57.png','R':'pal4/icon49.png',}
42 for s in stl:
43 stl_url='<Style id="'+stl[s]+'"><IconStyle><Icon><href>http://maps.google.com/mapfiles/kml/'+sty_pngs[s]+'</href> </Icon> </IconStyle></Style>'
44 exec('styl'+s+"='"+stl_url+"'")
45 exec('line.append(styl'+s+')')
46
計算經緯度
- 使用twd97模組
- 輸出時經緯度及高度間以逗點隔開
47 col=df.columns
48 lonlat=[]
49 #plot the placemarks
50 for i in range(len(df)):
51 nam=df.loc[i,col[2]]
52 desc=df.loc[i,col[3]]
53 sturl= '<styleUrl>#'+stl[NH]+'</styleUrl>'
54 line.append('<Placemark><name>'+nam+'</name><description>'+desc+'</description>'+sturl+'<Point><coordinates>')
55 if TWD97:
56 x,y=df.loc[i,col[0]],df.loc[i,col[1]]
57 lat,lon=twd97.towgs84(x,y)
58 if LL:
59 lon,lat=df.loc[i,col[0]],df.loc[i,col[1]]
60 slonlat=str(lon)+','+str(lat)+',0'
61 line.append(slonlat+'</coordinates></Point></Placemark>')
62 lonlat.append(slonlat)
63
附加軌跡線數據及檔尾
- 關鍵詞為
- 順序是軌跡線的經度、緯度、高度(0),跳行指令不一定需要。
64 #if with L in NorH, connection the marks with line
65 if 'L' in NorH:
66 line.append('<Placemark> <LineString> <coordinates>')
67 for i in range(len(df)):
68 line.append(lonlat[i]+'\n')
69 line.append('</coordinates></LineString></Placemark>')
70 line.append('</Document></kml>')
輸出KML檔案
- 基本上KML是一個文字檔,因此使用open.write指令即可將其寫出
71 with open(fname+'.kml','w') as f:
72 [f.write(l) for l in line]
Reference
- 名詞解釋
- ASCII(American Standard Code for Information Interchange,美国信息交换标准代码) https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/ASCII
- KML(Keyhole Markup Language Keyhole公司標記語言),wiki
- TWD97, 大地座標系統漫談, sunriver.com
- argparse
- pandas
- Pandas 基礎教學
- 10 minutes to pandas
- 資料科學家的 pandas 實戰手冊:掌握 40 個實用數據技巧
- KML and icons
- KML Samples - Google Developers
- KML Tutorial
- Google+Map讀取KML檔
- 在 Google 地球中匯入 KML 地圖資料 google support
- simplekml, pypi ;readthedoc
- google提供的icons
- twd97