Table of Contents
Swirl Overview
What is Metasearch? Is it the same as Federated Search?
Metasearch is a technical approach in which a search engine (or “broker”) accepts a query from some user (or system), distributes the query to other search engines, waits for the responses, then returns a normalized, unified and ideally relevancy-ranked set of results.
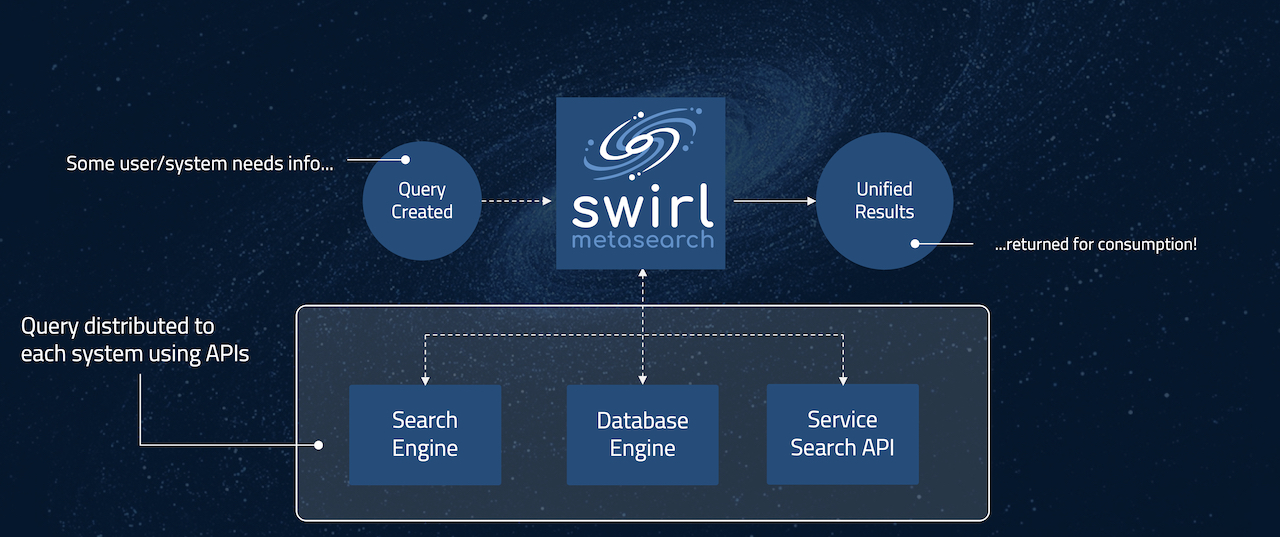
The metasearch approach differs from traditional enterprise search engines that process copies of all the source data and index it, which can be costly and time-consuming.
Metasearch leaves the source data in place and relies on each source’s own search engine to get access. This makes federated search less suited for deep navigation - across a large e-commerce or data set catalog, for example - but ideal for delivering cross-silo results with a fraction of the effort. It is also excellent for information enrichment, entity analysis (such as competitive, customer, industry or market intelligence) and integrating unstructured data for content curation, data science and machine learning applications.
What is Swirl?
Swirl is a metasearch engine built on the Python/Django stack and released under the Apache 2.0 license in 2022.
Swirl includes connectors to many popular systems including search engines, databases and other enterprise cloud services - anything with a query API.
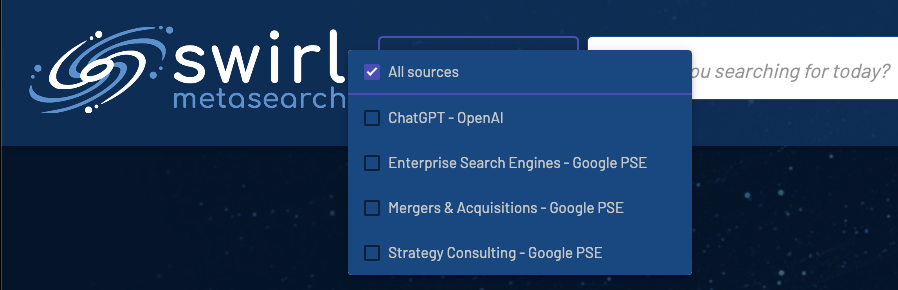
Use Swirl’s APIs to run searches and track their progress in real-time, then retrieve unified results re-ranked by Swirl’s built-in cosine-vector similarity model based on spaCy, plus term and phrase boosts.
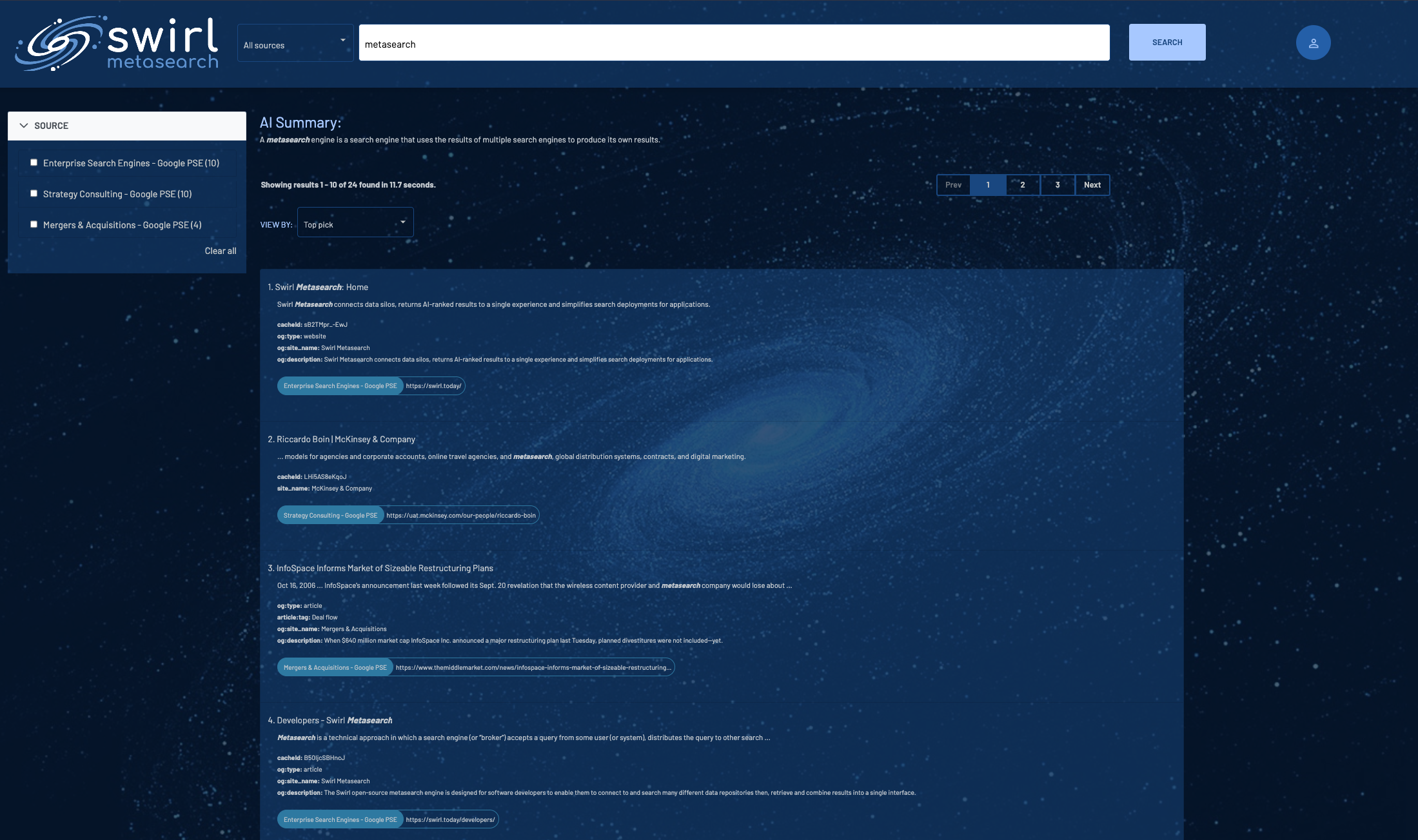
Swirl provides a swirl_score and swirl_rank for each item, as well as the original source’s ranking, so users can see instantly what was most relevant across all sources.
"results": [
{
"swirl_rank": 1,
"swirl_score": 1020.4933333333332,
"searchprovider": "Enterprise Search Engines - Google PSE",
"searchprovider_rank": 1,
"title": "Swirl <em>Metasearch</em>: Home",
"url": "https://swirl.today/",
"body": "Swirl <em>Metasearch</em> connects data silos, returns AI-ranked results to a single experience and simplifies search deployments for applications.",
"date_published": "unknown",
"date_published_display": "",
"date_retrieved": "2023-07-10 17:19:00.331417",
"author": "swirl.today",
...
},
Search developers can render Swirl’s JSON results in any existing UI or framework without having to normalize the field names. Data scientists and engineers, search managers, analysts and implementers who have worked with Elastic or Solr will find it easy to add results from any source with a typical search API to their existing search infrastructure.
What is Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)? Does Swirl support it?
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) is a machine learning framework that combines the strengths of pre-trained language models with external information retrieval systems to generate more informed and contextually relevant outputs.
RAG operates in two step:
Retrieve relevant documents based on the given input query
Use these retrieved passages as additional context when prompting generative AI
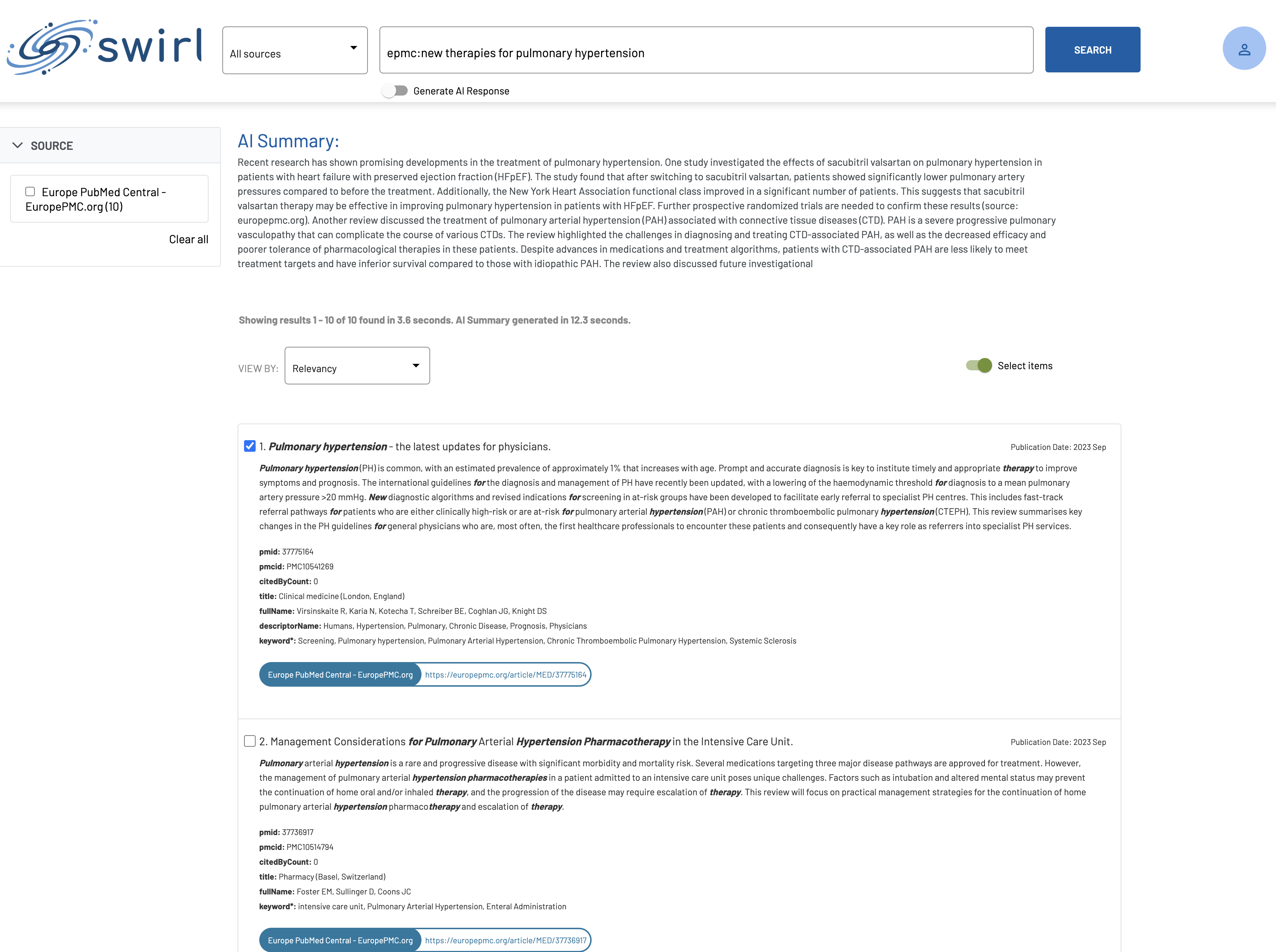
The results of RAG should always be an AI insight plus citations: the documents used in the prompt that create the insight, so the user can verify the results and, over time, learn to trust the RAG system.
The benefit of RAG is that it allows models to pull in real-world information that wasn’t present in their training data, thereby enhancing their capability to provide detailed and accurate answers. This approach bridges the gap between pure generation-based models and retrieval-based models, offering a hybrid solution that capitalizes on the strengths of both paradigms.
Swirl supports RAG as of Release 3.0. Refer to the AI Guide for more information.