Table of Contents
Developer Reference
Intended Audience
This guide is intended to provide developers with detailed reference information about Swirl. Please refer to the Developer Guide for an overview of how to work with Swirl.
State Table
The following table describes in more detail all the steps in the federation process, with the associated status and other important state information.
| Action | Module | Status | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Search object created | views.py SearchViewSet.list() | Search.status: NEW_SEARCH UPDATE_SEARCH | Required:Search.query_string |
| Pre-processing | search.py search() | Search.status: PRE_PROCESSING | Checks permissions Loads the Search object |
| Pre-query processing | search.py search() | Search.status: PRE_QUERY_PROCESSING | Processes Search.query_string and updates Search.query_string_processed |
| Federation | search.py search() | Search.status: FEDERATING FEDERATING_WAIT_* FULL_RESULTS | Creates one Connector for each SearchProvider in the Search |
| Connector Init | connectors/connector.py connectors/db_connector.py | Connector.status: INIT READY | Loads the Search and SearchProvider |
| Connector Federate | federate() | Connector.status: FEDERATING | |
| Connector Query Processing | process_query() | FEDERATING | Process Search.query_string_processed and store in Connector.query_string_to_provider |
| Connector Construct Query | construct_query() | FEDERATING | Take Connector.query_string_to_provider and create Connector.query_to_provider |
| Connector Validate Query | validate_query() | FEDERATING | Returns “False” if Connector.query_to_provider is empty |
| Connector Execute Search | execute_search () | FEDERATING | Connect to the SearchProvider Execute the search using Search.query_to_providerStore the response in Connector.response |
| Connector Normalize Response | normalize_response() | FEDERATING | Transform Connector.response into JSON list of dictsStore it in Connector.results |
| Connector Process Results | process_results() | Connector.status: FEDERATING READY | Process Connector.results |
| Connector Save Results | save_results() | Connector.status: READY | Returns “True” |
| Post-result processing | search.py search() | Search.status: POST_RESULT_PROCESSING FULL_RESULTS_READY FULL_UPDATE_READY | Runs the post_result_processorsUpdates Result objects |
Search.Status
Normal States
| Status | Meaning |
|---|---|
| NEW_SEARCH | The search object is to be executed immediately |
| UPDATE_SEARCH | The search object is to be updated immediately |
| PRE_PROCESSING | Swirl is performing pre-processing for this search |
| PRE_QUERY_PROCESSING | Swirl is performing pre-query processing for this search |
| FEDERATING | Swirl is provisioning Celery workers with Connectors and waiting for results |
| FEDERATING_WAIT_n | Swirl has been waiting for the number of seconds indicated by n |
| FULL_RESULTS | Swirl has received all results |
| NO_RESULTS | Swirl received no results |
| PARTIAL_RESULTS | Swirl has received results from some providers, but not all |
| POST_RESULT_PROCESSING | Swirl is performing post-result processing |
| PARTIAL_RESULTS_READY | Swirl has processed results from responding providers |
| PARTIAL_UPDATE_READY | Swirl has processed updated results from responding providers |
| FULL_RESULTS_READY | Swirl has processed results for all specified providers |
| FULL_UPDATE_READY | Swirl has processed updated results for all specified providers |
Error States
| Status | Meaning |
|---|---|
| ERR_DUPLICATE_RESULT_OBJECTS | More than one Result object was found; contact support for assistance. |
| ERR_NEED_PERMISSION | The Django User did not have sufficient permissions to perform the requested operation. More: Permissioning Normal Users |
| ERR_NO_ACTIVE_SEARCHPROVIDERS | Search failed because no specified SearchProviders were active |
| ERR_NO_RESULTS | Swirl has not received results from any source |
| ERR_NO_SEARCHPROVIDERS | Search failed because no SearchProviders were specified |
| ERR_RESULT_NOT_FOUND | A Result object that was expected to be found, was not; contact support for assistance. |
| ERR_RESULT_PROCESSING | An error occurred during Result processing - check the logs/celery-worker.log for details |
| ERR_SUBSCRIBE_PERMISSIONS | The user who created the Search object lacks permission to enable subscribe mode |
Key Module List
SearchProvider Object
A SearchProvider defines some searchable source. It includes metadata identifying the type of connector used to search the source and much more. Many properties are optional when creating a SearchProvider object. They will have the default values shown below.
Properties
| Property | Description | Default Value (Example Value) |
|---|---|---|
| id | Unique identifier for the SearchProvider | Automatic (1) |
| name | Human-readable name for the source | ”” ("Enterprise Search PSE") |
| owner | The username of the Django user that owns the object | Logged-in user ("admin") |
| shared | Boolean setting: if true the SearchProvider can be searched by other users, if false it is only available to the owner | true (false) |
| date_created | The time and date at which the SearchProvider was created | Automatic (2022-02-28T17:55:04.811262Z) |
| date_updated | The time and date at which the SearchProvdier was updated | Automatic (2022-02-29T18:03:02.716456Z) |
| active | Boolean setting: if true the SearchProvider is used, if false it is ignored when federating | false (true) |
| default | Boolean setting: if true the SearchProvider will be queried for searches that don’t specify a searchprovider_list; if false, the SearchProvider must be specified in the searchprovider_list | false (true) |
| connector | Name of the Connector to use for this source | ”” ("RequestsGet") |
| url | The URL or other string including file path needed by the Connector for this source; not validated | ”” ("https://www.googleapis.com/customsearch/v1") |
| query_template | A string with optional variables in form {variable}; the Connector will bind the query_template with required data including the url and query_string, as well as any query_mappings or credentials, at runtime. Note this format is not yet used by the Sqlite3 Connector. | ”” ("{url}?q={query_string}") |
| post_query_template | For the RequestsPost Connector: valid JSON and a marker for the query text which then sent as the POST body | ”” ("query": "{query_string}","limit": "100") |
| http_request_headers | A string for passing custom HTTP Request Header values to the source along with query | ”” ("Accept": "application/vnd.github.text-match+json") |
| query_processors | A list of processors to use to prepare the query for this source | ”” ("AdaptiveQueryProcessor") |
| query_mappings | A string defining the mappings for the query. Depends on the Connector used. | ”” ("cx=your-google-search-engine-key") |
| result_grouping_field | Used with the DedupeByFieldResultProcessor result processor, this string defines the specific source field to use for duplicate suppression. | ”” ("resource.conversationId") |
| result_processors | A list of processors to use to normalize results from this source | “CosineRelevancyResultProcessor” ("MappingResultProcessor","CosineRelevancyResultProcessor") |
| response_mappings | List of response keys and JSONPaths to transform this providers response into a JSON result set | ”” ("FOUND=searchInformation.totalResults, RETRIEVED=queries.request[0].count, RESULTS=items") |
| result_mappings | List of keys, optionally with values; see User Guide, Result Mappings for notes on special keys | ”” ("url=link,body=snippet,cacheId,NO_PAYLOAD") |
| results_per_query | The number of results to request from this source for each query | 10 (20) |
| credentials | The credentials to use for this source. Dependent on the source. | ”” ("key=your-google-json-api-key") |
| eval_credentials | A credential variable set in the session and then be used in the SearchProvider. | ”” ("session["my-connector-token"]") |
| tags | List of strings that organize SearchProviders into groups. | ”” ("News", "EnterpriseSearch") |
As of version 2.5, the revised CosineRelevancyResultProcessor must be added last to the list of result_processors.
APIs
| URL | Explanation |
|---|---|
| /swirl/searchproviders/ | List SearchProvider objects, newest first; create a new one using the POST button and the form at the bottom |
| /swirl/searchproviders/id/ | Retrieve a specific SearchProvider object; destroy it using the DELETE button; edit it using the PUT button and the form at the bottom |
Search Object
Search objects are JSON dictionaries that define the searches some user or system desires to have run. They have unique IDs. They may be linked to by Result objects.
The only required property is a query_string with the actual text to be searched. All other properties are optional when creating a Search object, and they will have default values shown below. As Swirl executes a search, asynchronously, it will update properties of the Search object like status and result_url in real-time.
Properties
| Property | Description | Default Value (Example Value) |
|---|---|---|
| id | Unique identifier for the Search | Automatic (search_id=1) |
| owner | The username of the Django user that owns the object | logged-in user (admin) |
| date_created | The time and date at which the Search was created | Automatic (2022-02-28T17:55:04.811262Z) |
| date_updated | The time and date at which the Search was updated | Automatic (2022-02-28T17:55:07.811262Z) |
| query_string | The query to be federated - the only required field! | ”” (knowledge management) |
| query_string_processed | The Search query, modified by any pre-query processing | ”” (“”) |
| sort | The type of search to be run | relevancy (date) |
| results_requested | The number of results, overall, the user has requested | 10 (25) |
| searchprovider_list | A list of the SearchProviders to search for this query; an empty list, the default, searches all sources | [] ([ "Enterprise Search Engines - Google PSE" ]) |
| subscribe | If True, Swirl will update this Search as per the Celery-Beats schedule | False (True) |
| status | The execution status of this search (see below) | NEW_SEARCH (FULL_RESULTS_READY) |
| pre_query_processors | A list of processors to apply to the query before federation starts | ”” ([ "SpellcheckQueryProcessor" ]) |
| post_result_processors | A list of result processors to apply to the results after federation is complete | ”” ([ "DedupeByFieldPostResultProcessor", "CosineRelevancyPostResultProcessor" ]) |
| result_url | Link to the initial Result object for the Search which uses the RelevancyMixer | Automatic ("http://localhost:8000/swirl/results?search_id=17&result_mixer=RelevancyMixer") |
| new_result_url | Link to the updated Result object for the search which uses the RelevancyNewItemsMixer | Automatic ("http://localhost:8000/swirl/results?search_id=17&result_mixer=RelevancyNewItemsMixer") |
| messages | Messages from SearchProviders | ”” (Retrieved 1 of 1 results from: Document DB Search) |
| result_mixer | The name of the Mixer object (see below) to use for ordering results | RoundRobinMixer (Stack2Mixer) |
| retention | The retention setting for this object; 0 = retain indefinitely; see Search Expiration Service for details | 0 (2 for daily deletion) |
| tags | Parameter (string) that can be passed into a search and will be attached to the Search object that is stored in Swirl | ”” ({ "query_string": "knowledge management", "tags": ["max_length:50"] }) |
There are some special Search tags that control query processing. For example, the SW_RESULT_PROCESSOR_SKIP Search tag can be used to skip a processor for the Search it is specified for: SW_RESULT_PROCESSOR_SKIP:DedupeByFieldResultProcessor
APIs
| URL | Explanation |
|---|---|
| /swirl/search/ | List Search objects, newest first; create a new one using the form at the bottom and the POST button |
| /swirl/search/id/ | Retrieve a specific Search object; destroy it using the DELETE button; edit it using the form at the bottom and the PUT button |
| /swirl/search/?q=some+query | Create a Search object with default values except for query_string which is set to the q= parameter value; return redirects to result set; also accepts providers parameter |
| /swirl/search/?qs=some+query | Create Search object as above, but return results synchronously; also accepts providers and result_mixer parameters |
| /swirl/search/?rerun=id | Re-run a Search, deleting any previously stored Results |
| /swirl/search/?update=id | Update a Search with new results since the last time you ran it |
Result Objects
A Result object is the normalized, re-ranked result for a single Search, from a single SearchProvider. They are created at the end of the federated search process in response to the creation of a Search object. They are the only Swirl object that has a foreign key (search.id).
Only Connectors should create Result objects.
Developers are free to operate on individual Results as needed for their application.
However, the goal of Swirl (and federated search in general) is to provide unified results from all sources. Swirl uses Mixers to make this quick and easy.
Properties
| Property | Description | Example Value |
|---|---|---|
| id | Unique identifier for the Result | 1 |
| owner | The username of the Django user that owns the object | admin |
| date_created | The time and date at which the Result was created. | 2022-02-28T17:55:04.811262Z |
| date_updated | The time and date at which the Result was updated | 2022-02-28T19:55:02.752962Z |
| search_id | The id of the associated Search; there may be many Result objects with this id | 18 |
| searchprovider | The name value of the SearchProvider that provided this result list | "OneDrive Files - Microsoft 365" |
| query_to_provider | The exact query sent to the SearchProvider | https://www.googleapis.com/customsearch/v1?cx=google-search-engine-id&key=google-json-api-key&q=strategy |
| query_processors | The names of the Processors, specified in the SearchProvider, that processed the query | "AdaptiveQueryProcessor" |
| result_processors | The names of the Processors, specified in the SearchProvider, that normalized the results | "MappingResultProcessor","CosineRelevancyResultProcessor" |
| result_processor_json_feedback | TBD | (See a full result object) |
| messages | A list of any messages (strings) from the SearchProvider | Retrieved 10 of 249 results from: OneDrive Files - Microsoft 365 |
| status | The readiness of the result set | READY |
| retrieved | The number of results Swirl retrieved from this SearchProvider for this query | 10 |
| found | The total number of results reported by the SearchProvider for this query | 2309 |
| time | The time it took for the SearchProvider to create this result set, in seconds | 1.9 |
| json_results | The normalized JSON results from this SearchProvider | (See below) |
json_results
| Field | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| swirl_rank | Swirl’s relevancy ranking for this result | 1 |
| swirl_score | A metric showing the relevancy of the result to the query. It is not meant to be meaningful as a number otherwise. It is only shown if &explain=True is set. | 1890.6471312936828 |
| searchprovider | The human-readable name for the SearchProvider | "OneDrive Files - Microsoft 365" |
| searchprovider_rank | The SearchProvider’s ranking of this result | 3 |
| title | The source-reported title for this result, with search term matches highlighted | German car industry to invest in <em>electric</em> <em>vehicles</em> ... |
| url | The URL for this result; may be reported by the source and/or calculated by Swirl | http://pwc.com/etc |
| body | The source-reported result snippet(s), with search term matches highlighted | <em>Technology</em> strategy encompasses a full set of Consulting capabilities ... |
| date_published | The source-reported time and date of publication of this result, when available (unknown if not). This is the field used by the DateMixer | unknown |
| date_published_display | Optional SearchProvider field for mapping a different publish date value for display purposes. | ... date_published=foo.bar.date1,date_published_display=foo.bar.date2 ... |
| date_retrieved | The time and date at which Swirl received this result from the source | 2022-02-20 03:45:03.207909 |
| author | The source-reported author of this result, when available | "CNN staff" |
| title_hit_highlights | TBD | TBD |
| body_hit_highlights | TBD | TBD |
| payload | A dictionary of all remaining keys in the SearchProvider’s response | {} |
| explain | A dictionary containing (a) the matching word stems, (b) similarity scores for each match in each field, (c) length adjustments and other metadata, (d) hits information. It is only shown if &explain=True is set. | {} |
Note that PAYLOAD can be totally different from SearchProvider to SearchProvider. It is up to the caller to access the PAYLOAD and extract whatever is needed, generally by making a new Processor (see below) or adding result_mappings.
APIs
| URL | Explanation |
|---|---|
| /swirl/results/ | List Result objects, newest first; create a new one using the POST button and form at bottom |
| /swirl/results/id/ | Retrieve a specific Result object; destroy it using the DELETE button; edit it using the PUT button and form at bottom |
| /swirl/results/?search_id=search_id | Retrieve unified Results for a specific Search, ordered by the Mixer specified; also accepts result_mixer and page parameters |
Connectors
Connectors are objects responsible for searching a specific type of SearchProvider, retrieving the results and normalizing them to the Swirl format. This includes calling query and result processors.
Both connector.py and db_connectory.py are base classes from which other connector classes are derived. While requests.py is a wrapper called by RequestsGet. Two utility functions, mappings.py and utils.py, can be used by other Connectors.
For Release 2.5.1, requests.py was updated to handle XML responses from source APIs and convert them to JSON for mapping in SearchProvider configurations.
The following table describes the included source Connectors:
| Connector | Description | Inputs |
|---|---|---|
| BigQuery | Searches Google BigQuery | query_template, credentials (project JSON token file) |
| ChatGPT | Asks OpenAI ChatGPT | credentials |
| Elastic | Searches Elasticsearch | url or cloud_id, query_template, index_name, credentials |
| Microsoft Graph | Uses the Microsoft Graph API to search M365 content | credentials |
| OpenSearch | Searches OpenSearch | url, query_template, index_name, credentials |
| PostgreSQL | Searches PostgreSQL database | url (connection parameters), query_template, credentials |
| RequestsGet | Searches any web endpoint using HTTP/GET with JSON response, including Google PSE, SOLR, Northern Light and more (see below) | url, credentials |
| RequestsPost | Searches any web endpoint using HTTP/POST with JSON response, including M365 | url, credentials |
| Sqlite3 | Searches SQLite3 databases | url (database file path), query_template |
Connectors are specified in, and configured by, SearchProvider objects.
BigQuery
The BigQuery connector uses the Google Cloud Python package.
The included BigQuery SearchProvider is intended for use with the Funding Data Set but can be adapted to most any configuration.
{
"name": "Company Funding Records - BigQuery",
"active": false,
"default": false,
"connector": "BigQuery",
"query_template": "select {fields} from `{table}` where search({field1}, '{query_string}') or search({field2}, '{query_string}');",
"query_processors": [
"AdaptiveQueryProcessor"
],
"query_mappings": "fields=*,sort_by_date=fundedDate,table=funding.funding,field1=company,field2=city",
"result_processors": [
"MappingResultProcessor",
"CosineRelevancyResultProcessor"
],
"result_mappings": "title='{company}',body='{company} raised ${raisedamt} series {round} on {fundeddate}. The company is located in {city} {state} and has {numemps} employees.',url=permalink,date_published=fundeddate,NO_PAYLOAD",
"credentials": "/path/to/bigquery/token.json",
"tags": [
"Company",
"BigQuery"
]
}
More information: BigQuery Documentation
ChatGPT
For Release 2.5.1, both the ChatGPT Connector and QueryProcessor were updated to use the ChatCompletion method which supports the latest GPT models, including GPT-4, and a much greater range of interactivity. The ChatGPT SearchProvider now queries the GPT-3.5-Turbo model by default.
The ChatGPT Connector makes use of the OpenAI APIs. It will return at most one result.
ChatGPT responses usually rank highly since they are written on-the-fly in response to the user’s query, reflect the terminology associated with that query, and are titled for the query.
The included SearchProvider is pre-configured with a “Tell me about: …” prompt. The ChatGPTQueryProcessor also contains other query options for ChatGPT.
{
"name": "ChatGPT - OpenAI",
"active": false,
"default": true,
"connector": "ChatGPT",
"url": "",
"query_template": "",
"query_processors": [
"AdaptiveQueryProcessor"
],
"query_mappings": "PROMPT='Tell me about: {query_to_provider}'",
"result_processors": [
"GenericResultProcessor",
"CosineRelevancyResultProcessor"
],
"response_mappings": "",
"result_mappings": "BLOCK=ai_summary",
"results_per_query": 10,
"credentials": "your-openai-API-key-here",
"tags": [
"ChatGPT",
"Question"
]
}
The Question and ChatGPT SearchProvider Tags make it easy to target ChatGPT by starting a query with either of them. For example:
Question: Tell me about knowledge management software?
You must remove the default result_mappings value of BLOCK=ai_summary in the SearchProvider configuration to enable the ChatGPT or Question Tags! Otherwise, these Tags will be ignored.
ChatGPT SearchProvider Tags
The following three Tags are available for use in the ChatGPT SearchProvider to help shape the Prompt or Default Role passed to ChatGPT along with the user’s query. To utilize these options:
- Add a valid OpenAI API Key to Swirl’s
.envfile (found in theswirl-homedirectory), and then restart the Swirl for it to take effect. - Add the
ChatGPTQueryProcessorto the SearchProvider query_processors list:"query_processors": [ "AdaptiveQueryProcessor", "ChatGPTQueryProcessor" ],
Available Tags
CHAT_QUERY_REWRITE_PROMPT: Override the default Prompt used to rewrite the query."CHAT_QUERY_REWRITE_PROMPT:Write a more precise query of similar length to this : {query_string}"CHAT_QUERY_REWRITE_GUIDE: Override thesystemrole passed to ChatGPT."CHAT_QUERY_REWRITE_GUIDE:You are a helpful assistant that responds like a pirate captain"CHAT_QUERY_DO_FILTER: Turn on or off the default internal filter of ChatGPT responses."CHAT_QUERY_DO_FILTER:false"
ChatGPT query_mapping
The following query_mapping is also available for use in the ChatGPT SearchProvider to help shape the Default Role passed to ChatGPT along with the user’s query. To utilize this query_mapping, add a valid OpenAI API Key to Swirl’s .env file (found in the swirl-home directory) and then restart the Swirl for it to take effect.
CHAT_QUERY_REWRITE_GUIDE: Override thesystemrole passed to ChatGPT."query_mappings": "PROMPT='Tell me about: {query_to_provider}',CHAT_QUERY_REWRITE_GUIDE='You are a helpful assistant that responds like a pirate captain'",
Elastic & OpenSearch
The Elastic and OpenSearch Connectors make use of each engine’s Python client.
Here is an example of a SearchProvider to connect to ElasticCloud using the cloud_id:
{
"name": "ENRON Email - Elastic Cloud",
"connector": "Elastic",
"url": "your-cloud-id-here",
"query_template": "index='{index_name}', query={'query_string': {'query': '{query_string}', 'default_field': '{default_field}'}}",
"query_processors": [
"AdaptiveQueryProcessor"
],
"query_mappings": "index_name=email,default_field=content,sort_by_date=date_published.keyword,NOT=true,NOT_CHAR=-",
"result_processors": [
"MappingResultProcessor",
"CosineRelevancyResultProcessor"
],
"result_mappings": "url=_source.url,date_published=_source.date_published,author=_source.author,title=_source.subject,body=_source.content,_source.to,NO_PAYLOAD",
"credentials": "(\"elastic\", \"elastic-password\")",
"tags": [
"Enron",
"Elastic"
]
}
This is the default OpenSearch SearchProvider that connects to a local instance of the engine:
{
"name": "ENRON Email - OpenSearch",
"active": false,
"default": false,
"connector": "OpenSearch",
"url": "http://localhost:9200/",
"query_template": "{\"query\":{\"query_string\":{\"query\":\"{query_string}\",\"default_field\":\"{default_field}\",\"default_operator\":\"and\"}}}",
"query_processors": [
"AdaptiveQueryProcessor"
],
"query_mappings": "index_name=email,default_field=content,sort_by_date=date_published.keyword,NOT=true,NOT_CHAR=-",
"result_processors": [
"MappingResultProcessor",
"CosineRelevancyResultProcessor"
],
"result_mappings": "url=_source.url,date_published=_source.date_published,author=_source.author,title=_source.subject,body=_source.content,_source.to,NO_PAYLOAD",
"credentials": "'admin','password'",
"tags": [
"Enron",
"OpenSearch"
]
}
Note the use of JSONPaths in the result_mappings. This is essential for Elastic and OpenSearch since they embed results in a _source field unless otherwise configured. For more details consult the User Guide, Result Mappings section.
Use the PAYLOAD Field to store extra content that doesn’t map to an existing item.
Microsoft Graph
The Microsoft Graph connector uses the Microsoft Graph API to query M365 content. The user must authenticate via OAuth2 in order to enable searching of their M365 content.
There are 5 pre-configured SearchProviders for querying the authenticated user’s M365 content:
- Outlook Messages
- Calendar Events
- OneDrive Files
- SharePoint Sites
- Teams Chat
{
"name": "Outlook Messages - Microsoft 365",
"active": false,
"default": true,
"connector": "M365OutlookMessages",
"url": "",
"query_template": "{url}",
"query_processors": [
"AdaptiveQueryProcessor"
],
"query_mappings": "NOT=true,NOT_CHAR=-",
"result_grouping_field": "conversationId",
"result_processors": [
"MappingResultProcessor",
"DedupeByFieldResultProcessor",
"CosineRelevancyResultProcessor"
],
"response_mappings": "",
"result_mappings": "title=resource.subject,body=summary,date_published=resource.createdDateTime,author=resource.sender.emailAddress.name,url=resource.webLink,resource.isDraft,resource.importance,resource.hasAttachments,resource.ccRecipients[*].emailAddress[*].name,resource.replyTo[*].emailAddress[*].name,NO_PAYLOAD",
"results_per_query": 10,
"credentials": "",
"eval_credentials": "",
"tags": [
"Microsoft",
"Email"
]
}
PostgreSQL
The PostgreSQL connector uses the psycopg2 driver.
Installing the PostgreSQL Driver
To use PostgreSQL with Swirl:
- Install PostgreSQL
- Modify the system PATH so that
pg_configfrom the PostgreSQL distribution runs from the command line - Install
psycopg2usingpip:
pip install psycopg2
- Uncomment the PostgreSQL Connector in the following modules:
# uncomment this to enable PostgreSQL
# from swirl.connectors.postgresql import PostgreSQL
CONNECTOR_CHOICES = [
('RequestsGet', 'HTTP/GET returning JSON'),
('Elastic', 'Elasticsearch Query String'),
# Uncomment the line below to enable PostgreSQL
# ('PostgreSQL', 'PostgreSQL'),
('BigQuery', 'Google BigQuery'),
('Sqlite3', 'Sqlite3')
]
- Run Swirl setup:
python swirl.py setup
- Restart Swirl:
python swirl.py restart
- Add a PostgreSQL SearchProvider like the one provided with the Funding Dataset
Suggestions on how to improve this process are most welcome!
Here is an example of a basic SearchProvider using PostgreSQL:
{
"name": "Company Funding Records - PostgreSQL",
"default": false,
"connector": "PostgreSQL",
"url": "host:port:database:username:password",
"query_template": "select {fields} from {table} where {field1} ilike '%{query_string}%' or {field2} ilike '%{query_string}%';",
"query_processors": [
"AdaptiveQueryProcessor"
],
"query_mappings": "fields=*,sort_by_date=fundedDate,table=funding,field1=city,field2=company",
"result_processors": [
"MappingResultProcessor",
"CosineRelevancyResultProcessor"
],
"result_mappings": "title='{company} series {round}',body='{city} {fundeddate}: {company} raised usd ${raisedamt}\nThe company is headquartered in {city} and employs {numemps}',date_published=fundeddate,NO_PAYLOAD",
"tags": [
"Company"
]
}
Note: Putting a fixed SQL query in the query_template is perfectly acceptable. Anything that doesn’t change in the URL can be stored here.
RequestsGet
The RequestsGet connector uses HTTP/GET to fetch URLs. It supports optional authentication. Here is a generic SearchProvider based on RequestsGet:
{
"name": "Sample HTTP GET Endpoint",
"connector": "RequestsGet",
"url": "http://hostname/site/endpoint",
"query_template": "{url}&textQuery={query_string}",
"query_processors": [
"AdaptiveQueryProcessor"
],
"query_mappings": "PAGE=start=RESULT_INDEX,DATE_SORT=sort=date",
"result_processors": [
"MappingResultProcessor",
"CosineRelevancyResultProcessor"
],
"response_mappings": "FOUND=count,RESULTS=results",
"result_mappings": "body=content,date_published=date,author=creator",
"credentials": "HTTPBasicAuth('your-username-here', 'your-password-here')",
"tags": [
"News"
]
}
Here is the same connector, configured for three different Google Programmable Search Engines:
[
{
"name": "Enterprise Search Engines - Google PSE",
"connector": "RequestsGet",
"url": "https://www.googleapis.com/customsearch/v1",
"query_template": "{url}?cx={cx}&key={key}&q={query_string}",
"query_processors": [
"AdaptiveQueryProcessor"
],
"query_mappings": "cx=0c38029ddd002c006,DATE_SORT=sort=date,PAGE=start=RESULT_INDEX,NOT_CHAR=-",
"result_processors": [
"MappingResultProcessor",
"DateFinderResultProcessor",
"CosineRelevancyResultProcessor"
],
"response_mappings": "FOUND=searchInformation.totalResults,RETRIEVED=queries.request[0].count,RESULTS=items",
"result_mappings": "url=link,body=snippet,author=displayLink,cacheId,pagemap.metatags[*].['og:type'],pagemap.metatags[*].['og:site_name'],pagemap.metatags[*].['og:description'],NO_PAYLOAD",
"credentials": "key=AIzaSyDvVeE-L6nCC9u-TTGuhggvSmzhtiTHJsA",
"tags": [
"News",
"EnterpriseSearch"
]
},
{
"name": "Strategy Consulting - Google PSE",
"connector": "RequestsGet",
"url": "https://www.googleapis.com/customsearch/v1",
"query_template": "{url}?cx={cx}&key={key}&q={query_string}",
"query_processors": [
"AdaptiveQueryProcessor"
],
"query_mappings": "cx=7d473806dcdde5bc6,DATE_SORT=sort=date,PAGE=start=RESULT_INDEX,NOT_CHAR=-",
"result_processors": [
"MappingResultProcessor",
"DateFinderResultProcessor",
"CosineRelevancyResultProcessor"
],
"response_mappings": "FOUND=searchInformation.totalResults,RETRIEVED=queries.request[0].count,RESULTS=items",
"result_mappings": "url=link,body=snippet,author=pagemap.metatags[*].['authors-name'],cacheId,pagemap.metatags[*].['articletype'],pagemap.metatags[*].['practice-name'],pagemap.metatags[*].['searchresults-tags'],pagemap.metatags[*].['site_name'],pagemap.metatags[*].['twitter:description'],NO_PAYLOAD",
"credentials": "key=AIzaSyDvVeE-L6nCC9u-TTGuhggvSmzhtiTHJsA",
"tags": [
"News",
"StrategyConsulting"
]
},
{
"name": "Mergers & Acquisitions - Google PSE",
"connector": "RequestsGet",
"url": "https://www.googleapis.com/customsearch/v1",
"query_template": "{url}?cx={cx}&key={key}&q={query_string}",
"query_processors": [
"AdaptiveQueryProcessor"
],
"query_mappings": "cx=b384c4e79a5394479,DATE_SORT=sort=date,PAGE=start=RESULT_INDEX,NOT_CHAR=-",
"result_processors": [
"MappingResultProcessor",
"DateFinderResultProcessor",
"CosineRelevancyResultProcessor"
],
"response_mappings": "FOUND=searchInformation.totalResults,RETRIEVED=queries.request[0].count,RESULTS=items",
"result_mappings": "url=link,body=snippet,author=pagemap.metatags[*].['article:publisher'],cacheId,pagemap.metatags[*].['og:type'],pagemap.metatags[*].['article:tag'],pagemap.metatags[*].['og:site_name'],pagemap.metatags[*].['og:description'],NO_PAYLOAD",
"credentials": "key=AIzaSyDvVeE-L6nCC9u-TTGuhggvSmzhtiTHJsA",
"tags": [
"News",
"MergersAcquisitions"
]
}
]
And here it is again, configured for SOLR with the tech products example collection installed:
{
"name": "techproducts - Apache Solr",
"active": false,
"default": false,
"connector": "RequestsGet",
"url": "http://localhost:8983/solr/{collection}/select?wt=json",
"query_template": "{url}&q={query_string}",
"query_processors": [
"AdaptiveQueryProcessor"
],
"query_mappings": "collection=techproducts,PAGE=start=RESULT_ZERO_INDEX,NOT=True,NOT_CHAR=-",
"result_processors": [
"MappingResultProcessor",
"CosineRelevancyResultProcessor"
],
"response_mappings": "FOUND=numFound,RESULTS=response.docs",
"result_mappings": "title=name,body=features,response",
"credentials": "",
"tags": [
"Products",
"Solr"
]
}
To adapt RequestsGet for your JSON response, just replace the JSONPaths on the right of the FOUND, RETRIEVED, and RESULT configurations in response_mappings, following the left-to-right format of swirl_key=source-key. If the response provides a dictionary wrapper around each result, use the RESULT path to extract it.
From there, map results fields to Swirl’s schema as described in the User Guide, Result Mapping section. Use the PAYLOAD Field to store any extra content from SearchProviders that doesn’t map to an existing Swirl field.
Add additional required key/value parameters to the url - if they won’t change from SearchProvider to SearchProvider - or by adding a mapping in the query_template and a default or guide value in the query_mappings. (See {collection} in the SOLR example above.)
RequestsPost
The RequestsPost connector uses HTTP/POST to submit search forms to configured URLs. It supports optional authentication. RequestsPost is used by M365 connectors and is now available for other sources. Here is a generic SearchProvider based on RequestsPost:
{
"name": "Sample HTTP POST Endpoint",
"active": false,
"default": false,
"connector": "RequestsPost",
"url": "https://xx.apis.it.h.edu/ats/person/v3/search",
"query_template": "{url}?Query={query_string}",
"query_processor": "",
"post_query_template": {
"fields": [
"names.personNameKey",
"names.firstName",
"names.lastName"
],
"conditions": {
"names.name": "*{query_string}*"
}
},
"query_processors": [
"AdaptiveQueryProcessor"
],
"query_mappings": "NOT=true,NOT_CHAR=-",
"result_processor": "",
"result_processors": [
"MappingResultProcessor",
"CosineRelevancyResultProcessor"
],
"response_mappings": "FOUND=count,RESULTS=results",
"result_mappings": "titles=names[0].name,url=names[0].personNameKey,body='{names[0].name} ID#: {names[*].personNameKey}'",
"results_per_query": 10,
"credentials": "X-Api-Key=<your-api-key>",
"eval_credentials": "",
"tags": [
"People"
]
}
Contact Support for help getting started.
SQLite3
The SQLite3 Connector uses the SQLite3 driver built-in to Python.
Here is an example of a SearchProvider using SQLite3:
{
"name": "Company Funding Records - SQLite3",
"active": false,
"default": false,
"connector": "Sqlite3",
"url": "db.sqlite3",
"query_template": "select {fields} from {table} where {field1} like '%%{query_string}%%' or {field2} like '%%{query_string}%%';",
"query_processors": [
"AdaptiveQueryProcessor"
],
"query_mappings": "fields=*,sort_by_date=fundeddate,table=funding,field1=city,field2=company",
"result_processors": [
"MappingResultProcessor",
"CosineRelevancyResultProcessor"
],
"result_mappings": "title='{company} series {round}',body='{city} {fundeddate}: {company} raised usd ${raisedamt}\nThe company is headquartered in {city} and employs {numemps}',date_published=fundeddate,NO_PAYLOAD",
"tags": [
"Company"
]
}
Note: Putting a fixed SQL query in the query_template is perfectly acceptable. Anything that doesn’t change in the URL can be specified here.
Processing Pipelines
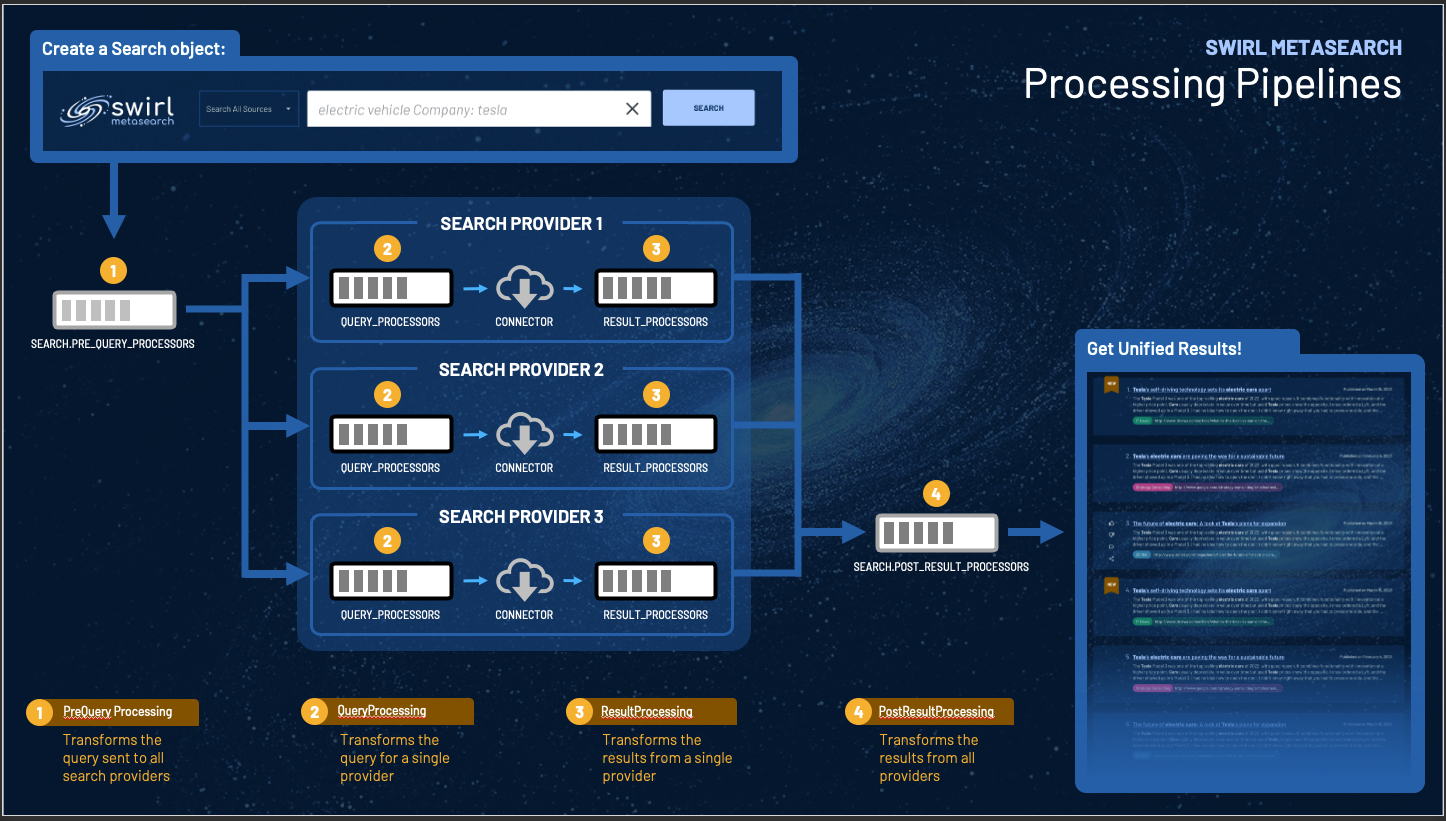
Processors are intended to be single purpose and executed in a sequence called a “pipeline”. Pipelines are specified as JSON lists in their respective properties. There are four processing pipelines in Swirl:
Search.pre_query_processorsSearchProvider.query_processorsSearchProvider.result_processorsSearch.post_result_processors
For example, the default Search.post_result_processors pipeline is:
"post_result_processors": [
"DedupeByFieldPostResultProcessor",
"CosineRelevancyPostResultProcessor"
],
This pipeline removes duplicates from the result set prior to relevancy ranking.
Query Processors
Query Processors operate queries. The exact field they operate on depends on how they are deployed.
| Pipeline | Reads | Updates |
|---|---|---|
| Search.pre_query_processors | Search.query_string | Search.query_string_processed |
| SearchProvider.query_processors | Search.query_string_processed | <Connector>.query_string_to_provider |
This table describes the query processors included in Swirl:
| Processor | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| AdaptiveQueryProcessor | Rewrites queries based on the query_mappings for a given SearchProvider | Should not be used as pre_query_processor |
| ChatGPTQueryProcessor | This query processor asks ChatGPT to rewrite queries based on a configurable prompt. For example it can rewrite queries to be fuzzier, broader, more specific, boolean, or in another language. | Experimental |
| GenericQueryProcessor | Removes special characters from the query | |
| SpellcheckQueryProcessor | Uses TextBlob to predict and fix spelling errors in query_string | Best deployed in a SearchProvider.query_processor for sources that need it; not recommended with Google PSEs |
Result Processors
Result Processors transform source results into the Swirl format defined in swirl/processors/utils.py.
The following table lists the Result Processors included with Swirl:
| Processor | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| GenericResultProcessor | Copies results from source format to Swirl format by exact match on name | Recommended for sources that don’t need mapping |
| MappingResultProcessor | Transforms results from source format to Swirl format, using SearchProvider.result_mappings | Default |
| LenLimitingResultProcessor | Checks if the title and body responses from a source exceed a configurable length (set in swirl_server/settings.py: SWIRL_MAX_FIELD_LEN = 512), truncates anything after that value, and adds an ellipsis (“…”). If the body field has been truncated, the processor reports the entire response in a new body_full field in the Payload. The default truncation length for can be overridden for a specific SearchProvider using a new Tag value (e.g. max_length:256). | Recommended for sources that consistently return lengthy title or body fields; should follow the MappingResultProcessor. |
| CleanTextResultProcessor | Removes non-alphanumeric characters from the source response. It should be considered for lengthy responses where URLs or other HTML or Markdown syntax appear in results. | Should be installed before the LenLimitingResultProcessor when both are used. |
| DateFinderResultProcessor | Looks for a date in any a number of formats in the body field of each result item. Should it find one, and the date_published for that item is 'unknown', it replaces date_published with the date extracted from the body, and notes this in the result.messages. | This processor can detect the following date formats:06/01/2306/01/202306-01-2306-01-2023jun 1, 2023june 1, 2023 |
Post Result Processors
PostResultProcessors operate only on processed result data and are saved to the Swirl database by each connector. They operate on Result objects.
CosineRelevancyPostResultProcessor
Swirl includes a cosine vector similarity relevancy model based on spaCy. The source code is found in: swirl/processors/relevancy.py
The relevancy model is as follows:
Matches on word stems from nltk
Scores the fields configured in
SWIRL_RELEVANCY_CONFIGin swirl_server/settings.pyAggregates the similarity of:
the entire query and the field, with the score being the highest in any single sentence (if any),
the entire query and a window of text around the field match
the 1 and 2 word combinations in the query (if long enough), and a window of text around the field match
Weights these fields as defined in
SWIRL_RELEVANCY_CONFIG, a dictionary structure in swirl_server/settings.pyFurther weights the window-text matches with the length of the match
Gives a small boost based on the original SearchProvider’s rank, equal to $1/(1+\sqrt{SearchProvider.rank})$
Normalizes the length of the result against the median length of all results in the set - this is reflected in the
result_length_adjustin theexplainstructure.Normalizes the query executed by this SearchProvider vs. all the other queries in the set - this is reflected in the
query_length_adjustin theexplainstructure.
The Swirl score is just that: a score. The higher a score is, the more contextually relevant the result is. Scores aren’t comparable between queries or results.
Tip: to translate a result score to a confidence score, take the #1 result as 1.0, and then divide subsequent results by the score for that result to calculate the confidence.
Swirl reports the swirl_rank, from 1 to N, where N is the total number of results. Swirl also includes the searchprovider_rank, which is the result rank assigned by the source. This makes it easy to compare what Swirl viewed as relevant compared to what each SearchProvider did.
In the event of a relevancy tie, the date_published and search_provider rank are used as additional sorts, to break it.
In Swirl 2.5, result processing was separated into two passes. The SearchProvider.result_processors runs first, followed by the Search.post_result_processors which adjusts length and finalizes. As a result of this change, the revised CosineRelevancyPostResultProcessor must be added last in the Search.post_result_processors list. For example:
"result_processors": [
"MappingResultProcessor",
"DateFinderResultProcessor",
"CosineRelevancyResultProcessor"
],
Mixers
The following table details the Result Mixers included with Swirl:
| Mixer | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| RelevancyMixer | Organizes results by relevancy score (descending), then source rank (ascending) | The default; depends on relevancy_processor being installed as the search.post_result_processors (also the default) |
| RelevancyNewItemsMixer | Organizes results as above, but hiding results that don’t have the new field as created during Search updates | This is the default for search.new_result_url |
| DateMixer | Organizes results by date_published. Results with “unknown” for date_published are omitted | Use when you want date sorted results |
| DateNewItemsMixer | Organizes results as above, but hiding results that don’t have the new field as created during Search updates | This is the default for search.new_result_url when search.date is set to sort |
| RoundRobinMixer | Organizes results by taking 1 result from each responding SearchProvider, alternating; actually calls Stack1Mixer (see below) | Good for searches with search.sort set to “date” or anytime you want a cross-section of results instead of just the ones with the most evidence |
| Stack1Mixer | Organizes results by taking 1 result from each responding SearchProvider, alternating | Good for cross-sections of data |
| Stack2Mixer | Organizes results by taking 2 from each responding SearchProvider, alternating | Good for cross-sections of data with 4-6 sources |
| Stack3Mixer | Organizes results by taking 3 from each responding SearchProvider, alternating | Good for cross-sections of data with few sources |
| StackNMixer | Organizes results by taking N from each responding source, where N if not specified is the number of results requested divided by the number of SearchProviders reporting at least 1 result | Good for cross-sections of data with few providers |
Date Mixer
If you want results sorted by date_published, descending, use the Date Mixer.
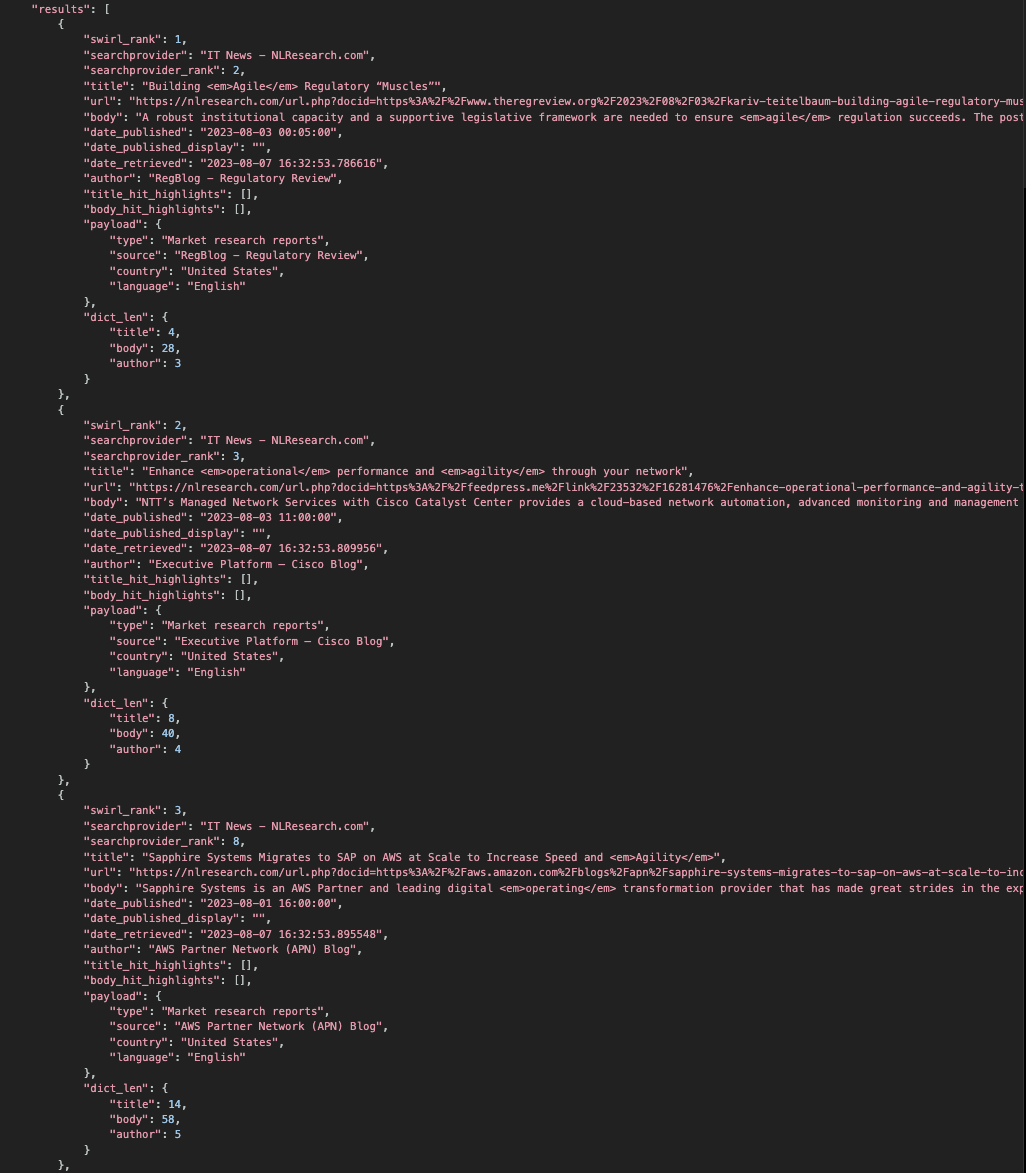
For example: http://localhost:8000/swirl/results?search_id=1&result_mixer=DateMixer
NewItems Mixers
The two NewItems mixers automatically filter results to items with the new field present. Both will report the number of results hidden because they do not have this field.
To remove the new field from all results in a search, add &mark_all_as_read=1 to the result_mixer URL property. For example:
http://localhost:8000/swirl/results/?search_id=1&result_mixer=DateNewItemsMixer&mark_all_as_read=1
The Mixer will then return 0 results. But it will return results if the Search is updated.
Mixer objects combine separate Result objects for a given Search, wrap them in metadata, and order them. For example, a Mixer might alternate from each source (Stack1Mixer), or sort results by date_published (DateMixer)
To invoke the mixer specified using the result_mixer property of the Search object, specify the search_id as shown in APIs, above:
http://localhost:8000/swirl/results/?search_id=1
If you use the Swirl defaults, a search will produce a JSON result that is relevancy ranked.
To specify a different Mixer, add &result_mixer=mixer-name to the URL.
http://localhost:8000/swirl/results/?search_id=1&result_mixer=Stack1Mixer
The following table describes the Mixer wrapper in more detail:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| messages | All messages from the Search and all SearchProviders |
| info | A dictionary of Found and Retrieved counts from each SearchProvider |
| info - search | Information about the Search, including the processed query, and links to re-run and re-score Searches |
| info - results | Information about the Results, including the number retrieved and the URL of the next (and previous) pages of results |
| results | Mixed Results from the specified Search |
Sample Data Sets
Funding Data Set
The TechCrunch Continental USA funding data set was taken from Insurity SpatialKey. It is included with Swirl in Data/funding_db.csv This file was processed with scripts/fix_csv.py prior to loading into SQLite3.
Loading into SQLite3
- Activate sqlite_web Then, from the swirl-home directory:
sqlite_web db.sqlite3 - A browser window should open automatically; if not go to http://localhost:8080/
Enter “funding” in the text box in the upper right of the screen and press the
Createbutton
Click
Choose Fileand select Data/funding_db.csvLeave “Yes” in the box below.
Click
Import.
- Load the Funding DB SQLite3 SearchProvider as described in the User Guide, SearchProvider section.
Loading into PostgreSQL
- Create a table following the structure in the CSV using SQL or something like Postico
-- DDL generated by Postico 1.5.21
-- Table Definition ----------------------------------------------
CREATE TABLE funding (
id integer GENERATED ALWAYS AS IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
permalink text,
company text,
numemps text DEFAULT '0'::numeric,
category text,
city text,
state text,
fundeddate date,
raisedamt numeric DEFAULT '0'::numeric,
raisedcurrency text,
round text
);
-- Indices -------------------------------------------------------
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX funding_pkey ON funding(id int4_ops);
- Run this SQL to ingest the CSV:
COPY funding(permalink,company,numemps,category,city,state,fundeddate,raisedamt,raisedcurrency,round) FROM '/path/to/Data/funding_db.csv' DELIMITER ',' CSV HEADER;
- Load the Funding DB PostgreSQL SearchProvider as described in the User Guide, SearchProvider section.
Loading into BigQuery
- Create a table with a schema like so:
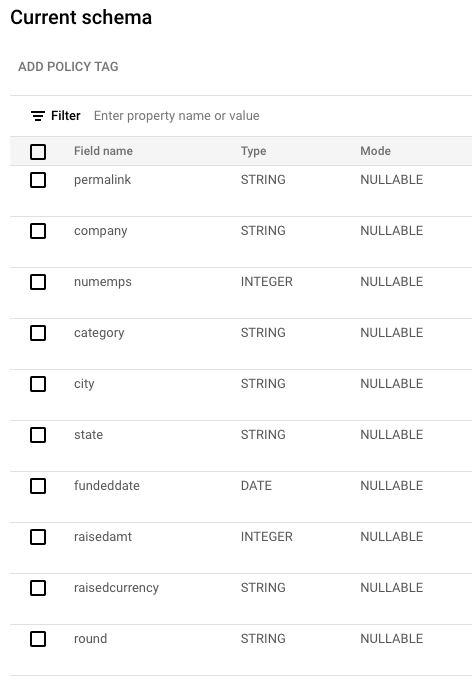
Load the CSV file into this table: Loading CSV data into a table
Load the Funding DB BigQuery SearchProvider as described in the User Guide, SearchProvider section.
Enron Email Data Set
This data set consists of 500,000+ emails from 150 employees of the former Enron Corporation. It’s available from Kaggle: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/wcukierski/enron-email-dataset among other places.
Loading into Elastic or OpenSearch
Download the enron email data set: https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~enron/
Unzip and untar the download and place the
email.csvfile in your swirl-home directoryCreate a new Elastic/OpenSearch index named ‘email’ using the development console:
PUT /email
- Index the
emails.csvfrom the Swirl directory:
For Elastic:
python scripts/index_email_elastic.py emails.csv -p elastic-password
For OpenSearch:
python scripts/index_email_opensearch.py emails.csv -p admin-password
The script will report progress every 100 rows. Hit Ctrl-C to stop it if desired.
- Verify that the messages have been indexed by Elastic/OpenSearch by querying in the development console:
GET _search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
Results should appear in the right-hand pane:
{
"took" : 38,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 6,
"successful" : 6,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 6799,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.0,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : ".kibana_92668751_admin_1",
"_id" : "config:2.4.1",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"config" : {
"buildNum" : 4665
},
"type" : "config",
"references" : [ ],
"migrationVersion" : {
"config" : "7.9.0"
},
"updated_at" : "2023-01-18T02:36:57.349Z"
}
},
{
"_index" : "email",
"_id" : "c13MwoUBmlIzd81ioZ7H",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"url" : "allen-p/_sent_mail/118.",
"date_published" : "2000-09-26 09:26:00.000000",
"author" : "Phillip K Allen",
"to" : "pallen70@hotmail.com",
"subject" : "Investment Structure",
"content" : """---------------------- Forwarded by
...etc...